In the context of electrical engineering, a transformer is a static electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Here are the key components and functions of a transformer:
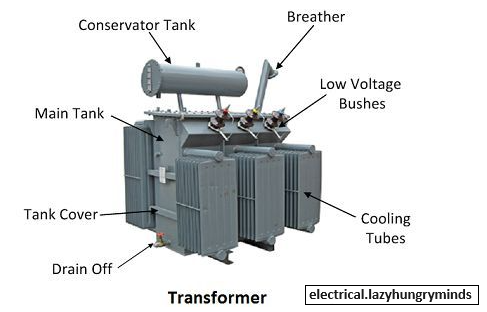
- Basic Components:
- Primary Winding: The coil which receives energy from the AC source.
- Secondary Winding: The coil which delivers energy to the load.
- Core: Made of laminated iron or other magnetic materials, the core provides a path for the magnetic flux.
- Working Principle: Transformers operate on the principle of mutual induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a varying magnetic field. This magnetic field induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary winding, thus transferring energy.
- Types of Transformers:
- Step-Up Transformer: Increases voltage from primary to secondary winding.
- Step-Down Transformer: Decreases voltage from primary to secondary winding.
- Isolation Transformer: Transfers power between two circuits without changing voltage levels but isolates the circuits.
Leave a Reply