Dynamic braking resistors are electrical devices used in braking systems to dissipate the excess energy generated by electric motors or generators during the braking process. When an electric motor or generator is decelerating or braking, it acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy. This electrical energy needs to be dissipated to prevent damage to the braking system or the connected power supply.
Connection Diagram of DBR with VFD
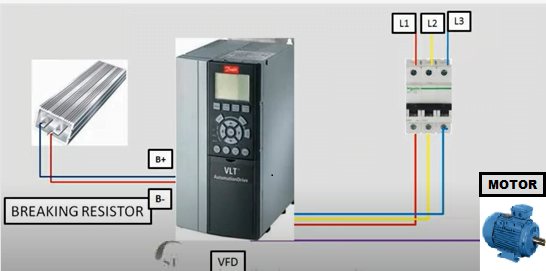
Dynamic braking resistors are designed to absorb and dissipate this excess electrical energy as heat. They are typically made of resistive elements, such as grids or wire-wound resistors, housed in a protective enclosure. When the braking action is engaged, the electrical energy is directed through the dynamic braking resistors, which offer a high resistance to the flow of current. This causes the electrical energy to be converted into heat, which is then dissipated into the surrounding environment.
By using dynamic braking resistors, the braking energy is effectively converted into thermal energy, allowing for controlled deceleration and preventing overvoltage conditions in the electrical system. These resistors are commonly employed in applications such as electric trains, elevators, cranes, and other industrial machinery that require precise braking control and energy dissipation.
Here are some common applications of dynamic braking resistors:
- Electric Trains and Locomotives: Dynamic braking resistors are extensively used in electric trains and locomotives to assist in braking and deceleration. They help dissipate the excess energy generated during regenerative braking, where the electric motors act as generators, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy.
- Elevators and Escalators: Dynamic braking resistors are employed in elevator and escalator systems to control and dissipate the energy generated during braking or deceleration. They help ensure smooth and controlled stopping of the elevator cars or escalator steps.
- Cranes and Hoists: Cranes and hoists often use dynamic braking resistors to control the deceleration and braking of heavy loads. They enable safe and controlled lowering of loads, dissipating the excess energy generated during the braking process.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): In electric vehicles, dynamic braking resistors, also known as regenerative braking resistors, are used to manage the energy generated during regenerative braking. They help to dissipate the excess energy and prevent overvoltage conditions in the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Wind Turbines: Large-scale wind turbines employ dynamic braking resistors to control and dissipate the excess energy generated during high wind conditions or system faults. This ensures the stability and safe operation of the wind turbine.
- Industrial Machinery: Various industrial applications, such as conveyors, cranes, machine tools, and robotic systems, utilize dynamic braking resistors to control the braking and deceleration of motors. They help prevent electrical system damage and provide precise control over the motion of heavy machinery.
Overall, dynamic braking resistors find applications in any system that requires controlled braking, deceleration, and energy dissipation in electrical motors or generators.
Leave a Reply