Electricity generation in a thermal power plant involves the conversion of heat energy into electrical energy. The basic principle behind this process is to use a heat source to produce steam, which is then used to drive a turbine connected to a generator. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how electricity is generated in a thermal power plant.
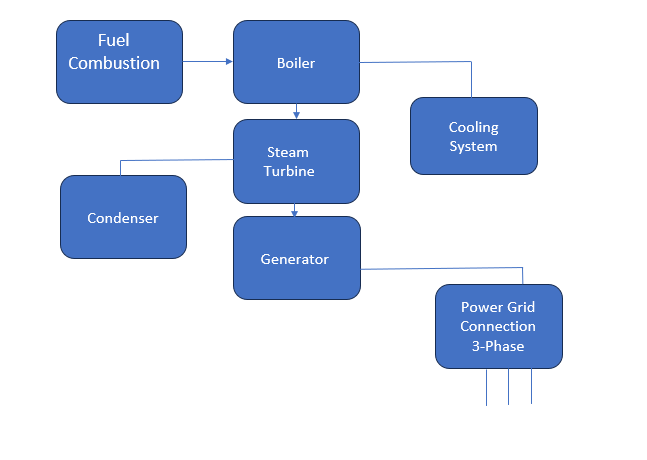
- Fuel Combustion:
- The most common fuels used in thermal power plants are coal, natural gas, oil, or even biomass.
- The fuel is burned in a combustion chamber, releasing a large amount of heat energy.
- Boiler:
- The heat generated from fuel combustion is used to produce high-pressure and high-temperature steam in a boiler.
- The boiler is a large vessel where water is heated to produce steam.
- Steam Turbine:
- The high-pressure steam is directed towards the blades of a turbine.
- The force of the steam causes the turbine blades to rotate.
- Generator:
- The rotating turbine is connected to a generator.
- As the turbine spins, it turns the rotor inside the generator, inducing a flow of electrons and generating an electric current.
- Condenser:
- After passing through the turbine, the steam is condensed back into water in a condenser.
- The condensation process releases heat, which is usually transferred to a cooling medium (such as water or air).
- Cooling System:
- A cooling system is employed to condense the steam and convert it back into water.
- The cooling medium absorbs the heat from the steam, allowing it to condense.
- Water Circulation:
- The condensed water is then returned to the boiler to be heated again, completing the water-steam cycle.
- Power Grid Connection:
- The generated electrical energy is then fed into the power grid for distribution to homes, industries, and other consumers.
This process is known as a Rankine cycle, and it is the fundamental principle behind most thermal power plants. The efficiency of the overall system depends on various factors, including the type of fuel, the design of the plant, and the technology used in the turbines and generators.
Leave a Reply